Connect Snowflake
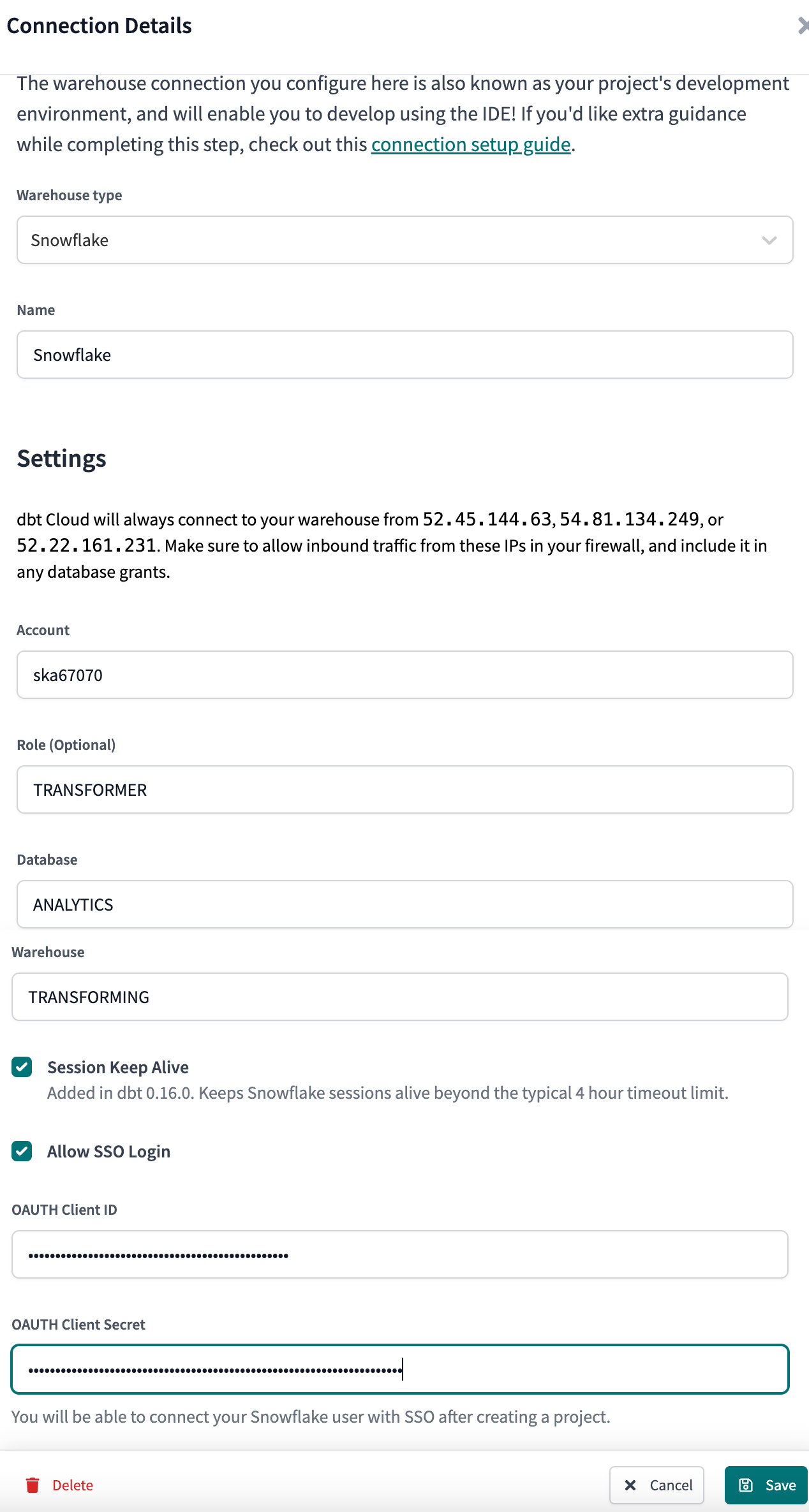
The following fields are required when creating a Snowflake connection
| Field | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Account | The Snowflake account to connect to. Take a look here to determine what the account field should look like based on your region. | |
| Role | A mandatory field indicating what role should be assumed after connecting to Snowflake | transformer |
| Database | The logical database to connect to and run queries against. | analytics |
| Warehouse | The virtual warehouse to use for running queries. | transforming |
Note: A crucial part of working with dbt atop Snowflake is ensuring that users (in development environments) and/or service accounts (in deployment to production environments) have the correct permissions to take actions on Snowflake! Here is documentation of some example permissions to configure Snowflake access.
Authentication methods
This section describes the different authentication methods available for connecting dbt Cloud to Snowflake.
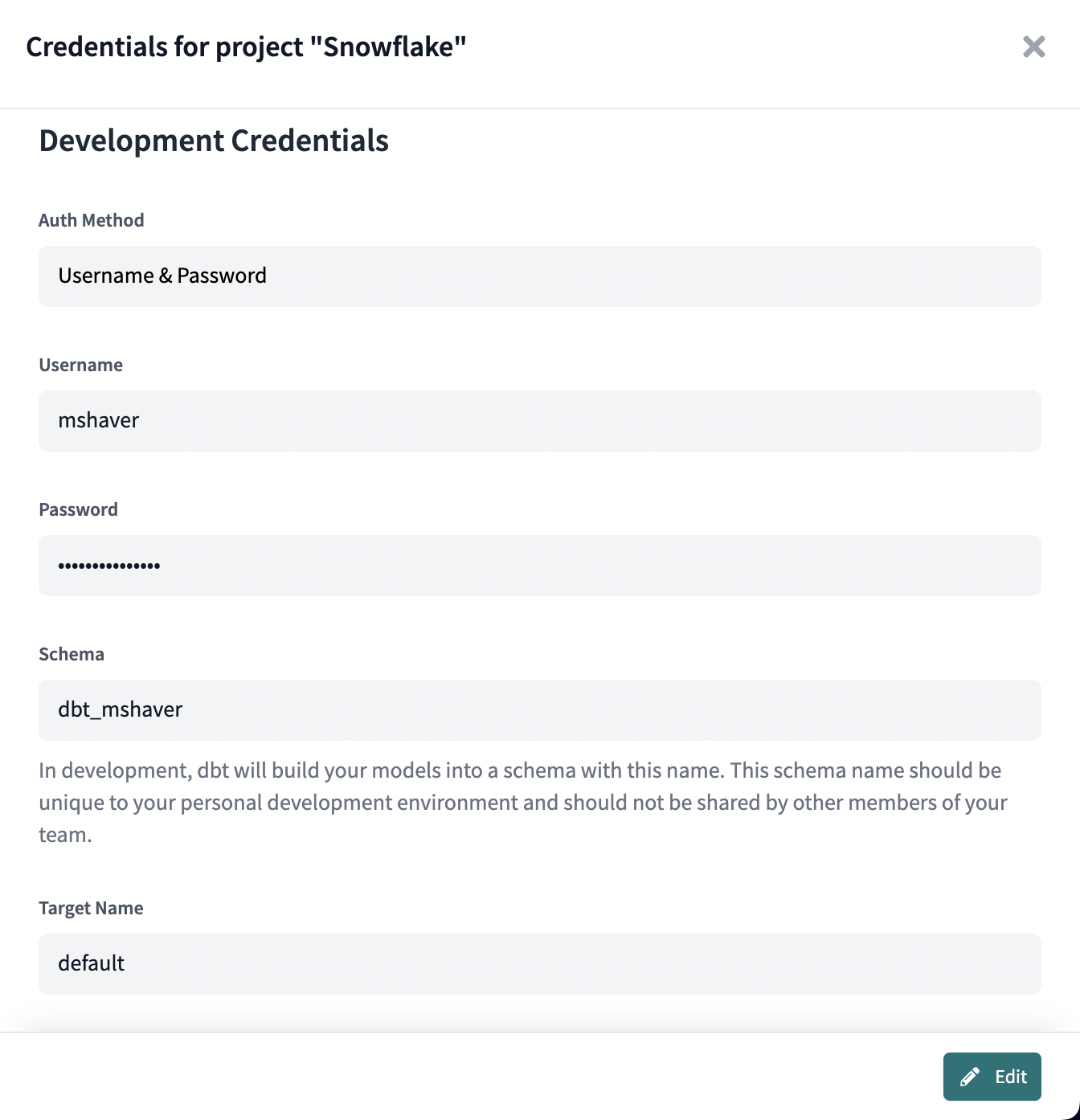
Username / Password
Available in: Development environments, Deployment environments
The Username / Password auth method is the simplest way to authenticate
Development or Deployment credentials in a dbt project. Simply enter your Snowflake
username (specifically, the login_name) and the corresponding user's Snowflake password
to authenticate dbt Cloud to run queries against Snowflake on behalf of a Snowflake user.
Note: The schema field in the Developer Credentials section is a required field.
Snowflake MFA
Prerequisites:
- A development environment in a dbt Cloud project
- The Duo authentication app
- Admin access to Snowflake (if MFA settings haven't already been applied to the account)
- Admin (write) access to dbt Cloud environments
dbt Cloud supports Snowflake's multi-factor authentication (MFA) as another username and password option for increased login security. Snowflake's MFA support is powered by the Duo Security service.
-
In dbt Cloud, set the following extended attribute in the development environment General settings page, under the Extended attributes section:
authenticator: username_password_mfa -
To reduce the number of user prompts when connecting to Snowflake with MFA, enable token caching in Snowflake.
-
Optionally, if users miss prompts and their Snowflake accounts get locked, you can prevent automatic retries by adding the following in the same Extended attributes section:
connect_retries: 0
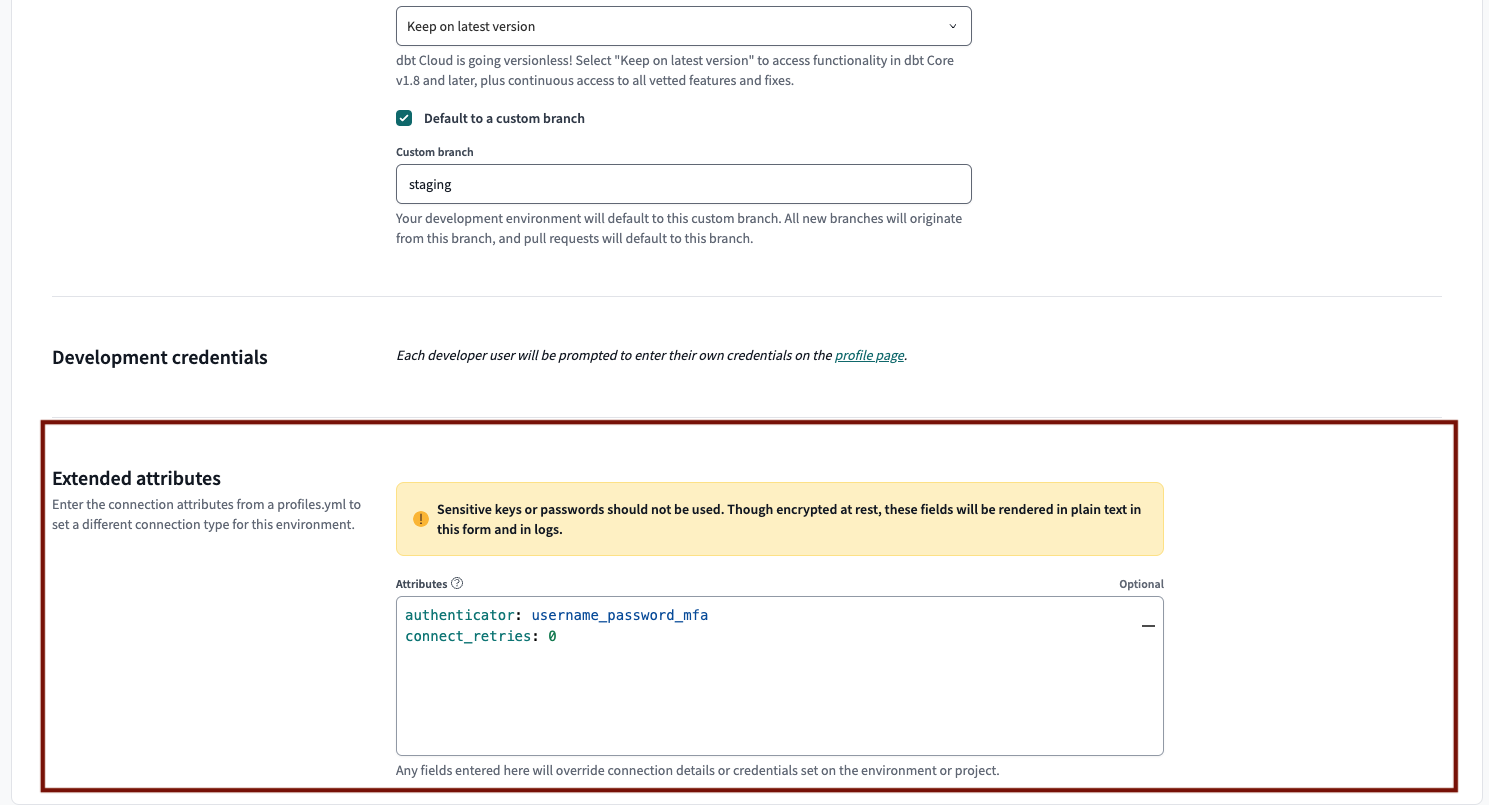 Configure the MFA username and password, and connect_retries in the development environment settings.
Configure the MFA username and password, and connect_retries in the development environment settings.Key pair
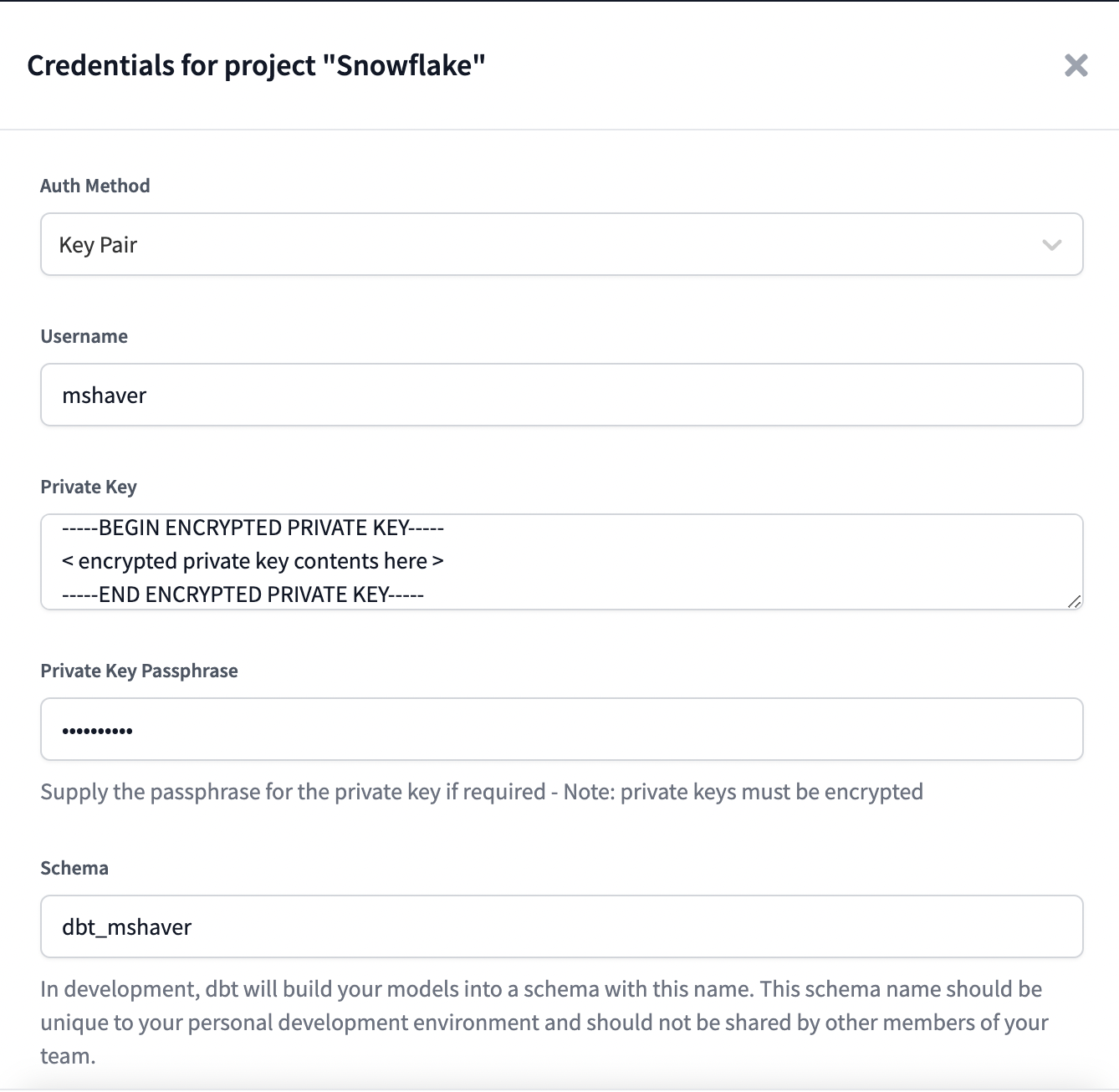
Available in: Development environments, Deployment environments
The Keypair auth method uses Snowflake's Key Pair Authentication to authenticate Development or Deployment credentials for a dbt Cloud project.
-
After generating an encrypted key pair, be sure to set the
rsa_public_keyfor the Snowflake user to authenticate in dbt Cloud:alter user jsmith set rsa_public_key='MIIBIjANBgkqh...'; -
Finally, set the Private Key and Private Key Passphrase fields in the Credentials page to finish configuring dbt Cloud to authenticate with Snowflake using a key pair.
- Note: Unencrypted private keys are permitted. Use a passphrase only if needed. Starting from dbt version 1.7, dbt introduced the ability to specify a
private_keydirectly as a string instead of aprivate_key_path. Thisprivate_keystring can be in either Base64-encoded DER format, representing the key bytes, or in plain-text PEM format. Refer to Snowflake documentation for more info on how they generate the key.
- Note: Unencrypted private keys are permitted. Use a passphrase only if needed. Starting from dbt version 1.7, dbt introduced the ability to specify a
-
To successfully fill in the Private Key field, you must include commented lines. If you receive a
Could not deserialize key dataorJWT tokenerror, refer to Troubleshooting for more info.
Example:
-----BEGIN ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----
< encrypted private key contents here - line 1 >
< encrypted private key contents here - line 2 >
< ... >
-----END ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----
Snowflake OAuth
Available in: Development environments, Enterprise plans only
The OAuth auth method permits dbt Cloud to run development queries on behalf of a Snowflake user without the configuration of Snowflake password in dbt Cloud.
For more information on configuring a Snowflake OAuth connection in dbt Cloud, please see the docs on setting up Snowflake OAuth.
Configuration
To learn how to optimize performance with data platform-specific configurations in dbt Cloud, refer to Snowflake-specific configuration.
Custom domain URL
To connect to Snowflake through a custom domain (vanity URL) instead of the account locator, use extended attributes to configure the host parameter with the custom domain:
host: https://custom_domain_to_snowflake.com
This configuration may conflict with Snowflake OAuth when used with PrivateLink. IF users can't reach Snowflake authentication servers from a networking standpoint, please contact dbt Support to find a workaround with this architecture.
Troubleshooting
If you're receiving a Could not deserialize key data or JWT token error, refer to the following causes and solutions: